INTRODUCTION
Antrochoanal polyps (ACPs) are benign polypoid lesions arising from the maxillary antrum and they extend into the choana. ACPs usually have two components and these are the cystic and solid polypoid parts (1-4). ACPs are almost always unilateral, although bilateral ACPs have been reported in literature (5, 6). They most commonly occur in children and young adults. The most common presenting symptoms are nasal obstruction and nasal drainage. Nasal endoscopy and computed tomography (CT) scans are required for making the diagnosis and the treatment planning. The differential diagnosis should include different causes of unilateral nasal obstruction and ipsilateral nasal masses (1-3). ACPs are treated with surgery.
The purpose of this study was to review the epidemiology, etiopathogenesis, clinical features, the preoperative evaluation, pathology, differential diagnosis, treatment and complications of ACPs.
TERMINOLOGY AND EPIDEMIOLOGY
ACP or Killian polyp arises from the inflamed and edematous mucosa of the maxillary antrum and they consist of two components; the antral one is almost always cystic and the other is solid. ACP passes through the maxillary ostium into the middle meatus, with extension into the nasopharynx or oropharynx. The cystic component mostly originates from the posterior, inferior, lateral or medial walls of the maxillary antrum, and it attaches to the solid polyp with a pedicle in the nasal cavity (1-4, 7-9). Lee and Huang (2) found that the most common site of origin was the posterior wall (92%).
ACPs usually originate from the nasal septum, sphenoid sinus, ethmoid sinus, hard and soft palates and nasal turbinates (10-14). ACPs are mostly seen unilaterally, but rare cases of bilateral ACPs have been reported in the literature (5, 6).
It was reported that ACPs constitute approximately 4-6% of all nasal polyps in the general population (1, 3, 8, 15), yet Cook et al. (4) found a higher incidence of ACPs (10.4%). This rate increases to 33% in children (1, 15, 16), and ACPs occur more commonly in children and young adults (1, 3, 8), but it may manifest at any age (4, 8, 17, 18). In a previous study, approximately 70% of patients were between 30 and 70 yr old (4). ACPs are more common in males than females (1, 4, 8, 18, 19). Cook et al. (4) observed that the incidence of ACPs was 70% in males and 30% in females.
ETIOPATHOGENESIS
The etiopathogenesis of ACPs has not been clarified (1-4, 9). Chronic sinusitis and allergy have been implicated (1-4, 8, 9). Lee and Huang (2) determined that 65% of the patients with ACP had chronic sinusitis. ACPs, which could develop from an expanding intramural cyst in the maxillary sinus, may result in maxillary sinusitis and ostiomeatal complex disease when the polyp expands to impede the maxillary sinus ostium or hinder the mucociliary function of the sinus mucosa. Chronic maxillary sinusitis, instead of being the cause of ACPs, could be the result of an obstruction of the maxillary sinus ostium by ACPs (2, 20). Some authors have found a statistically significant association of ACP with allergic diseases (4, 15). Cook et al. (4) reported allergic rhinitis in approximately 70% of their patients with ACP. Similarly, Chen et al. (15) detected that allergic disease plays a significant role in ACP. On the other hand, other authors have found no association of ACP with allergy (7, 21).
CLINICAL FEATURES AND PREOPERATIVE EVALUATION
Taking a careful history, a complete physical examination, nasal endoscopy and radiological examinations are necessary for diagnosing and planning treatment of ACPs. The presenting symptoms are similar to many of the nasal disorders, and these include nasal obstruction, rhinorrhea, snoring, headache, mouth breathing, epistaxis, anosmia, halitosis, dyspnea, dysphagia, dysphonia and nasal pruritis (1, 3, 12, 24). Nasal obstruction and nasal drainage are the most common presenting symptoms. Orvidas et al. (25) noted nasal obstruction (100%), rhinorrhoea (48%), snoring (36%) and mouth breathing (32%) in their patients with ACP. Also, obstructive sleep apnoea and cachexia due to ACP have been reported in the literature (26, 27).
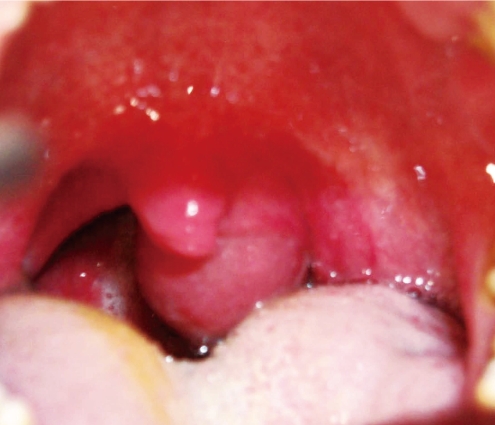
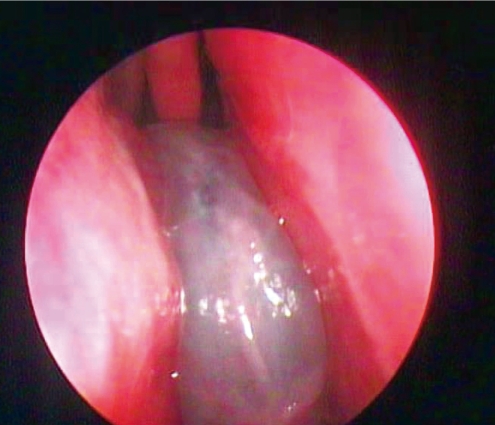
Anterior rhinoscopy usually reveals an intranasal polypoidal mass (18). A larger polyp may extend into the nasopharynx and the polyp may be seen by posterior rhinoscopy or in the mouth (8) (Fig. 1). Nasal endoscopy and CT are the main diagnostic techniques. ACPs typically appear as a smooth, bluish or yellowish mass on nasal endoscopy (18) (Fig. 2).
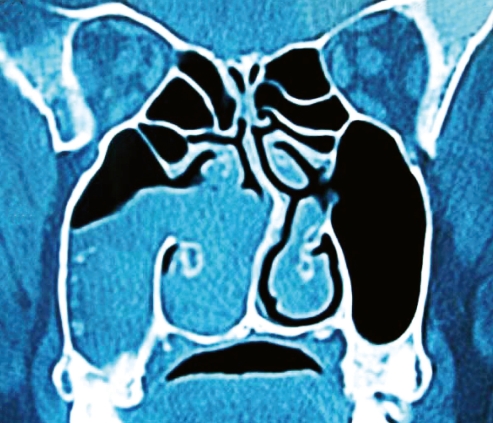
On CT scans, ACPs are seen as soft tissue masses that occupy the maxillary antrum and extend through the natural or accessory maxillary ostium into the nasal cavity between the middle turbinate and the lateral nasal wall (Fig. 3), without bone erosion or expansion, and they may extend posteriorly toward the choana (2, 28) (Fig. 4).
HISTOPATHOLOGIC EXAMINATION
The histopathological characteristics of ACPs are similar to those of non-allergic polyps of the maxillary sinus (7, 30). ACPs are lined with pseudostratified ciliated epithelium, and their stromal connective tissue contains a variable infiltration of infiammatory cells (30). The stroma is usually edematous and highly vascular, and it is composed of loose connective tissue that is mainly infiltrated with plasma cells and a few eosinophils. The inflammatory cell infiltration was more severe and the eosinophilic infiltration was less severe in ACPs when compared with that of allergic nasal polyps (7, 9). There are significantly less submucosal glands in the ACPs compared to that of nasal polyps (9, 21). Aktas et al. (21) reported that the surface epitelial cells of ACP patients have few or no cilia, and the stroma contains a minimal number of mucous glands with eosinophils. Skladzien et al. (30) reported that scanning electron microscopic examination of ACPs reveals squamous cell metaplasia less frequently than inflammatory polyps, and ACPs are mostly covered with normal ciliated respiratory epithelium. They also reported that there were minor differences in the composition of the cellular infiltration on light microscopic examination.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
The differential diagnosis of ACPs should include juvenile angiofibroma, nasal glioma, meningoencephalocele, inverted papilloma, mucocele, mucus retention cyst, Tornwalt's cyst, grossly enlarged adenoids, lymphoma and nasopharyngeal malignancies (1-3, 8, 28, 31).
Mucus retention cyst occurs following obstruction of the mucus-secreting glands within sinuses, and particularly in the maxillary sinus antrum. It is a mucus-filled epithelial cyst arising from the walls of the sinus cavity, and it does not extend into the choana (31). A crescent-shape air rim above the cyst usually allows making the differential diagnosis (28).
Mucocele contains mucus and desquamated epithelium and mucoceles can fill sinus cavities. It usually occurs in the frontoethmoid region. Mucoceles rarely appear in the maxillary sinuses and they do not extend through the choana. When the mucocele causes enlargement of the cavity, it causes erosion or sclerosis of the walls of the cavity. If a mucocele is infected, then it becomes a mucopyocele (28, 31).
Angiofibroma is a vascular, benign neoplasm that has the potential for local destruction, and this may arise from the nasal pterygoid plate. It affects male adolescents. The symptoms may be epistaxis, nasal obstruction or a mass in the nasopharynx. Carotid angiography and CT scanning may be used for making the differential diagnosis from other lesions (18, 31). It has a homogeneous density and it enhances strongly following administration of intravenous contrast.
Hemangioma is a rare benign vascular lesion in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. Most of them arise from the anterior nasal septum and the nasal turbinates (28).
Malignant tumors of the nasopharynx may cause difficulty when making the differential diagnosis. Malignant tumors of the nasopharynx account for about 1% of all malignancies (31). These tumors cause airway obstruction, destruction of bony structures and invasion into the paranasal sinuses. CT scanning can be useful to evaluate the location and size of the lesion and the extent of the neoplastic involvement. The most common malignant tumors are lymphoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, lymphoepithelioma, esthesioneuroblastoma and chordoma (31). Esthesioneuroblastoma arises from the olfactory mucosa and it is classically located in the roof of the nasal cavity (28).
TREATMENT AND COMPLICATIONS
The treatment of ACP is always surgical. Simple polypectomy and a Caldwell Luc procedure were the previously preferred methods for surgically treating ACPs. In recent yr, functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) became the more preferred surgical technique. Simple polypectomy carries a high recurrence rate (2, 4, 19, 32). The antral part of the polyp should be removed to avoid post-operative recurrence. There is controversy concerning the route of removal of the antral part. The Caldwell-Luc procedure offers good exposure for complete removal of the antral part of the polyp (15). But this procedure may have possible complications, including cheek anaesthesia, cheek swelling and injury of the infraorbital nerve, and it carries the risk of damaging the growing teeth and the growth centers of the maxilla in children (1, 3, 18, 32).
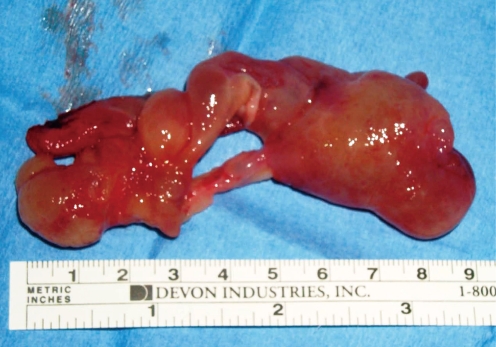
FESS has recently been shown to be a safe and effective method for treating ACPs, and it consists of resection of the nasal part of the polyp and the cystic antral part with attachment to the maxillary wall via the middle meatus (18, 19, 32-35) (Fig. 5). The lower part of the uncinate process is removed and then the maxillary ostium is widened. Cook et al. (4) observed no recurrences for 33 patients with ACPs after FESS. Ozer et al. (33) performed FESS, combined FESS and transcanin sinoscopy or the Caldwell Luc approach for the treatment of ACPs. They found recurrence in 3 patients after FESS, yet they found no recurrence after combined FESS and transcanin sinoscopy or the Caldwell Luc approach. Atighechi et al. (34) used a mini-Caldwell approach with FESS in their patients. They reported the technique showed minimal recurrence and a low complication rate, and so the technique is useful to completely remove ACPs. Hong et al. (36) recommended powered instrumentation during FESS as an effective technique for removing ACPs and the antral portion. They found an improvement rate of 96.4% and no significant complications when powered instrumentation was used. El-Guindy and Mansour (35) used combined endoscopic middle meatal surgery and transcanine sinoscopy to remove the residual tissue of ACPs in the antrum. Lee and Huang (2) used the transnasal endoscopic approach for ACPs originating from the inferior and posterior walls of the maxillary sinus and they used the combined endoscopic and transcanine approach for ACPs originating from the lateral walls of the maxillary sinus and for the recurrent patients. They reported the success rate of the transnasal endoscopic approach and the combined endoscopic and transcanine approach as 76.9% and 100%, respectively.
CONCLUSION
ACPs are benign polypoid lesions arising from the maxillary antrum and they extend into the choana. The most common presenting symptoms are nasal obstruction and nasal drainage. ACPs should be considered in the differential diagnosis of unilateral nasal obstruction and a nasal mass. ACPs can be diagnosed by taking a careful history and conducting clinical exams and nasal endoscopic and radiological examinations. FESS for complete removal of ACPs is an extremely safe and effective procedure. Physicians should focus on detecting the exact origin and extent of the polyp to prevent recurrence. Powered instrumentation during FESS is an effective technique for removing ACPs and the antral portion.